



The first part of a SQL query that is run is the FROM clause. The FROM clause tells SQL which table or tables you want to get data from. The syntax for a FROM clause getting data from a single table is provided below:
/* This code tells SQL which table to get our data from */
FROM people;
Practice typing in the table name you want to select:
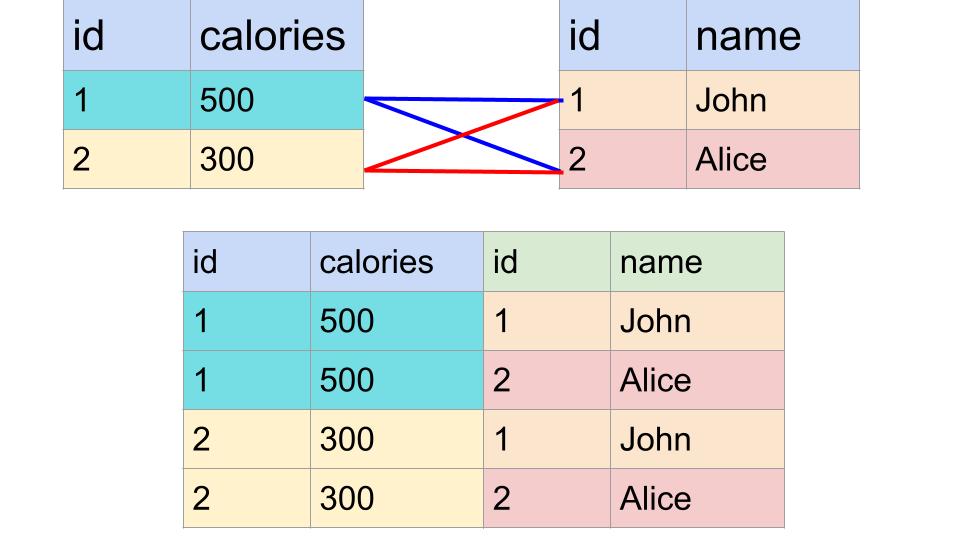
FROM| ID | Calories |
|---|---|
| 1 | 500 |
| 2 | 300 |
| ID | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | John |
| 2 | Alice |
Sometimes we want to get data from multiple tables. The simplest way to do this is with a cross join. A cross join of two tables yields a table where each row is a combination of a row of table 1 and a row in table 2. The cross join forms a row for every possible pariing of rows from the two tables. Here is a visual demonstration where the blue line represents combinations for the first two rows of the cross join and the red lines represent combinations for the last two rows of the cross join:
Here is the syntax to write a cross join:
/* Write a cross join with commas */
FROM player, teams;
/* Write a cross join with the keywords "CROSS JOIN" */
FROM player CROSS JOIN teams;